Describe the structure and function of major and subcellular organelles STEM_BIO1112-Ia-c-2. Which of the following is the typical feature of a prokaryotic cell.

Structures External To The Cell Wall Prokaryotic Cell Cell Wall Bacterial Cell Structure
Prokaryotes domains Archaea and Bacteria are single-celled organisms that lack a nucleus.
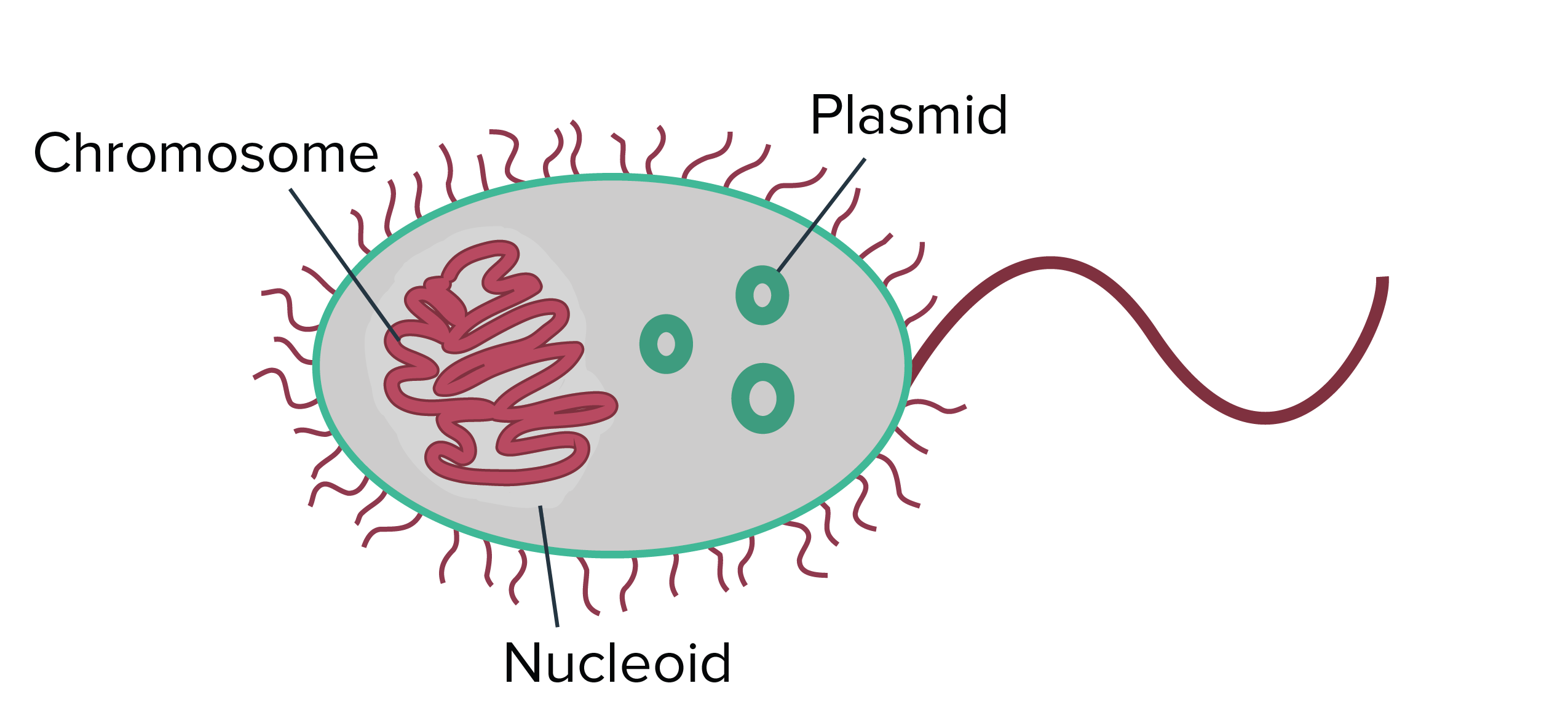
. All prokaryotes have chromosomal DNA localized in a nucleoid ribosomes a cell membrane and a cell wall. The cytoplasm a jelly-like substance inside the cell. Internal Structures of Prokaryotic Cells Plasma Membrane.
The cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells has a high concentration of dissolved solutes. Part A Drag the labels to the appropriate locations in this diagram. Each of these structures and cellular components plays a critical role in the growth survival.
It requires students to identify different types of eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. B absence of nucleus. The other structures shown are present in some but not all bacteria.
The cell wall acts as an extra. D absence of cell wall. However all cells have four common structures.
A darkened region called the nucleoid Figure 2. Membrane Transport Diffusion Osmosis can be defined as. Prokaryotic DNA is found in the central part of the cell.
Can you label the structures of a prokaryotic cell. Water Balance in Cells The ideal osmotic environment for an animal cell is ISOTONIC environment An animal cell places HYPOTONIC solution will gain watersweel. Prokaryotic DNA is found in a central part of the cell.
The other structures shown are present in some but not all bacteria. C absence of RNA. We will discuss where these different types of cells are found.
There are many differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Start studying Label the Structures of the Prokaryotic Cell. Most prokaryotes have a cell wall that lies outside the boundary of the plasma membrane.
This figure shows the generalized structure of a prokaryotic cell. Functions of Membrane Proteins BioFlix Activity. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools.
Biology questions and answers. And ribosomes where protein synthesis takes. This Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Worksheet is a great way to review prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
After going through this module you are expected to. Tour of an Animal Cell Cell Structures Can. A absence of DNA.
This includes a nucleus. Focus will move to eukaryotic cells and the organelles in them. The chief molecules in cells are nucleic acids proteins and polysaccharides.
MCQ on Prokaryotic Cell Structure. Part A Drag the labels to the appropriate locations in this diagram. All prokaryotes have chromosomal DNA localized in a nucleoid ribosomes a cell membrane and a cell wall.
The other structures shown are present in some but not all bacteria. Many prokaryotes also have a cell wall and capsule. All prokaryotes have chromosomal DNA localized in a nucleoid ribosomes a cell membrane and a cell wall.
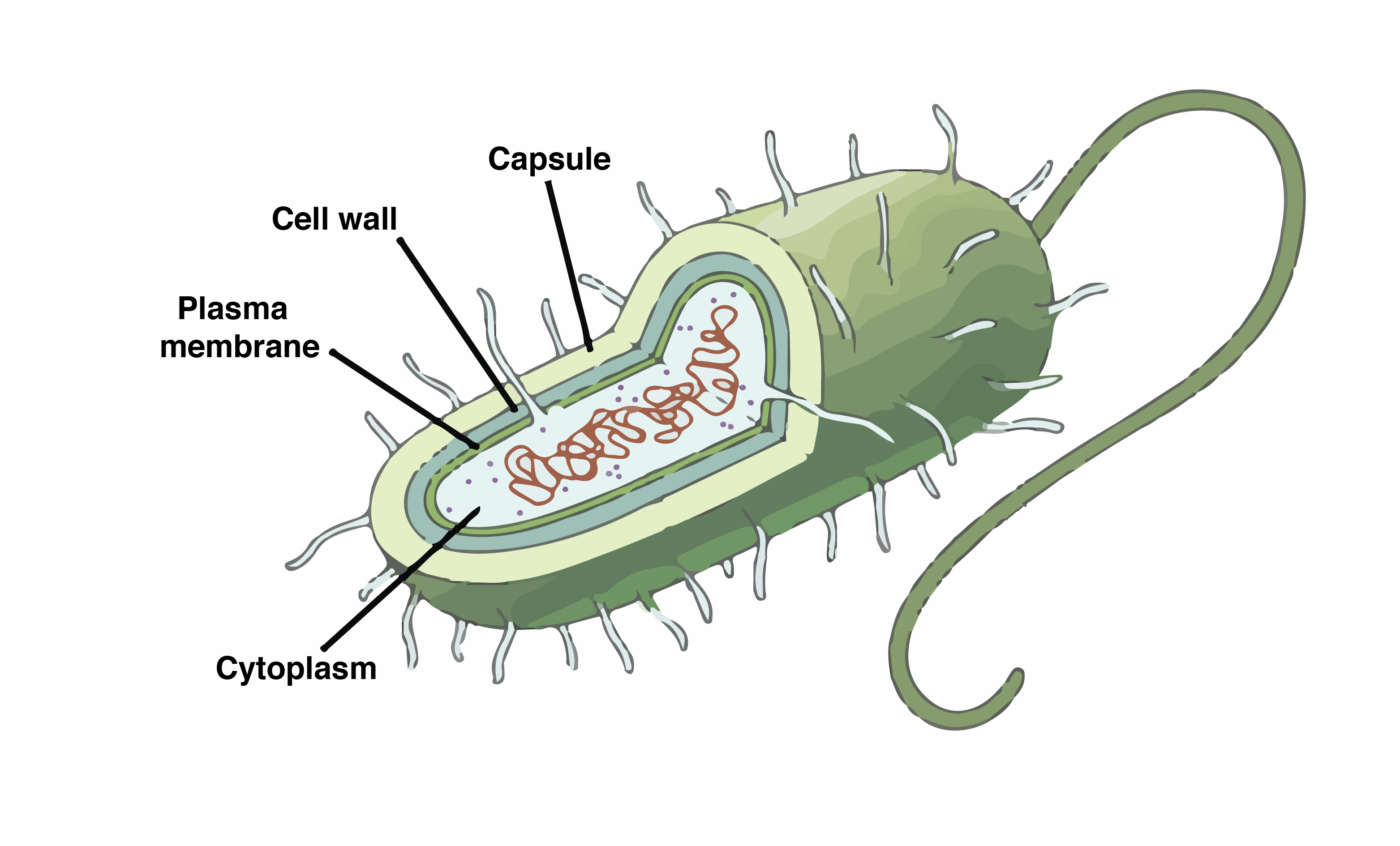
The Cell Wall. The plasma membrane which functions as a barrier for the cell and separates the cell from its environment. This includes a nucleus.
It is essentially the bag that holds all of the intracellular material and regulates the. Eukaryotic cells on the other hand contain many membrane-bound. The cell membrane is a double-layer of phospho lipids with associated proteins and other molecules.
Prokaryotic cells lack structures referred to as membrane-bound organelles. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. Therefore they do not have a nucleus but instead generally have a single chromosome.
Prokaryotes are unicellular organisms that lack organelles or other internal membrane-bound structures. Therefore the osmotic pressure within the cell is relatively high. Some prokaryotes have flagella pili or fimbriae.
Flagella are used for locomotion while most pili are used to exchange genetic material during a type of reproduction called conjugation. Proteins that are needed for a specific function or that are involved in the same biochemical pathway are encoded together in blocks called operonsFor example all of the genes needed to use lactose as an energy source are coded next to each other in the. The worksheet is ideal for grades 6-8.
They have a single piece of circular DNA in the nucleoid area of the cell. Start studying Structures of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells and their Functions. A piece of circular double-stranded DNA located in an area of the cell called the nucleoid.
Though the structures of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells differ see prokaryote eukaryote their molecular compositions and activities are very similar. This figure shows the generalized structure of a prokaryotic cell. A cell is bounded by a membrane that enables it to exchange certain materials with its surroundings.
Genetic material DNA and RNA Some prokaryotic cells also have other structures like the cell wall pili singular pillus and flagella singular flagellum. Explain the postulates of the Cell Theory STEM_BIO1112-Ia-c-1. Unlike prokaryotic cells in which DNA is loosely contained in the nucleoid region eukaryotic cells possess a nucleus which is surrounded by a complex nuclear membrane that houses the DNA genome Figure 359By containing the cells DNA the nucleus ultimately controls all activities of the cell and also serves an essential role in reproduction and heredity.
Most prokaryotes have a cell wall outside the plasma membrane. Some prokaryotes may have additional structures such as a capsule flagella and pili. The region in prokaryotic cell where double.
This figure shows the generalized structure of a prokaryotic cell. There are four main structures shared by all prokaryotic cells bacterial or archaean. The cell wall is a protective layer that surrounds some cells and gives them shape and rigidity.
Distinguish prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells according to their distinguishing features STEM_BIO1112-Ia-c-3. Reset Helio capsule timbrie Homes plama membrane Rucold bacten apote Parduction Submit Previous Answers Flequest Answer. It includes multiples choice and truefalse.
Nucleic acids the genetic material of the cell. Students will be given a diagram of eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells and asked to list the differences using a T chart provided while we go through a power point presentation. The DNA of prokaryotes is organized into a circular chromosome supercoiled in the nucleoid region of the cell cytoplasm.
Most prokaryotes have a peptidoglycan cell wall and many have a polysaccharide capsule. Structures of a Prokaryotic Cell Can you label the structures of a prokaryotic cell. Most prokaryotes have a peptidoglycan cell wall and many have a polysaccharide capsule.
Chapter 5docx - Chapter 5 Learning through Art.

Prokaryote Structure Article Khan Academy

0 Comments